Uterine fibroids are the most common benign (not cancerous) tumors of the uterus (womb). They account for 5% of all gynaecological visits.
Fibroids are hormone dependant tumors and grow with stimulation by estrogen. They may grow as single or multiple tumors, and often shrink after menopause.
Risk factors associated with the development of fibroids:
- Overweight/obesity
- Early onset of periods (before age of 10)
- No previous pregnancies
- Ethnicity (African, Asian)
Common symptoms of uterine fibroids:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic/abdominal pain
- A sensation of “fullness”
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Pressure on nearby organs with consequences such as frequent urination, inability to pass urine, infertility, miscarriage, and preterm labour
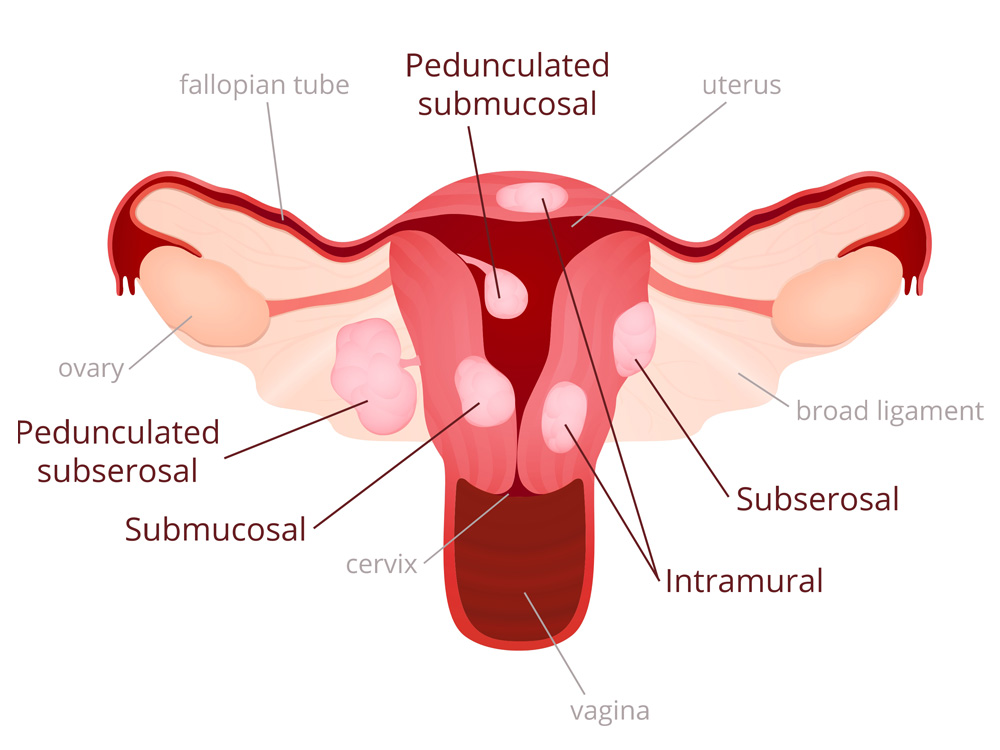
Not all fibroids have to be treated as many are asymptomatic. For those that need treatment there are a few possible options available, including:
- Hysteroscopic resection (for intra-cavity fibroids)
- Fibroid embolisation (radiology guided treatment)
- Myomectomy (removal of the fibroids with preservation of the uterus)
- Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus)
The method of treatment is dictated by your symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, age and desire to preserve fertility. This can all be discussed with your gynaecologist.

